Algae as Health Food
The development of algae supplements, such as chlorella, Dunaliella, spirulina, and Euglena, which we discuss this time, is active, with new products being proposed daily. As each algae has different nutrients, supplements are supplied for various purposes. It is rare for the same algae to produce different compositions, and research is progressing to open up new applications. In this reported study, it was discovered that Euglena, when cultivated with “bonito broth” and intense red light, produced components that Euglena had not made before.
The Nutritional Value of Euglena and the Potential for New Nutritional Values
Euglena, as food, reportedly contains a balanced mix of 59 types of nutrients, including 13 vitamins, 9 minerals, 19 amino acids, 12 types of unsaturated fatty acids such as DHA and EPA, and paramylon, a type of dietary fiber (according to Euglena Co., Ltd.). By forming the powder into supplements or mixing it into food, the nutritional value of the food can be enhanced. While Euglena’s nutritional value has already been evaluated, it has been reported that different species of Euglena not used as food can produce different nutritional components due to differences in the cultivation environment. Therefore, conditions to produce new nutrients have been explored in Euglena species that have already been consumed.
“Bonito Broth” + “Intense Red Light”
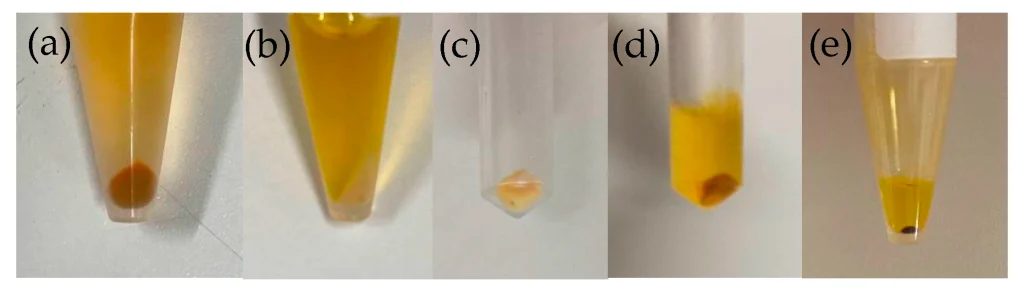
In the experiment, “bonito broth” was used as the culture medium. Bonito broth contains amino acids, peptides, inosinic acid, alkaline substances, trace vitamins, and minerals, providing sufficient nutrients for cultivating Euglena. Additionally, the light color was changed to “red” and irradiated intensely.
As a result, Euglena (Euglena gracilis) changed into red cells. Originally, the green color of Euglena is chlorophyll, but it was decomposed in this culture system. Furthermore, the substance causing the red color was identified as “diadinoxanthin,” a carotenoid pigment not previously seen in Euglena. Reddened Euglena is expected to become a supplement demonstrating new functionalities. Future research is promising.

Hopes for Physical Improvement in Substance Production in Plants and Algae
Among the components utilized by humans, many are difficult to synthesize chemically and are efficiently synthesized by microorganisms like plants and algae. Moreover, in modern times, more efficient substance production has become possible through genetic engineering. On the other hand, this study showed that it is possible to make algae produce new components by changing the cultivation environment and conditions. Since it does not involve genetic modification, the research and development period is shortened, significantly speeding up the time to market. It seems likely that more components produced through a similar scheme will increase in the future. The addition of new options for substance production expands business opportunities. The potential of chloroplast-containing organisms, including Euglena, seems to be still largely untapped.

コメント