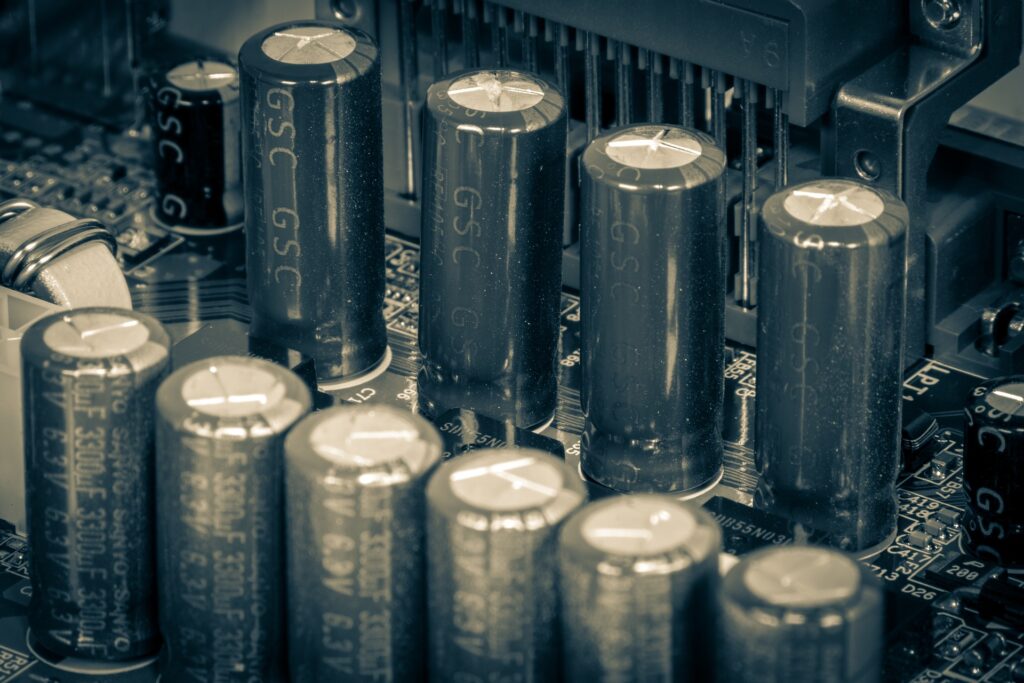
What is a capacitor?
Do you know what a “capacitor” is? It is also called a condenser. A capacitor is an electronic component that stores electrical charge and can release power instantly. Its basic structure consists of two conductor plates (electrodes) facing each other, with an insulator (dielectric) sandwiched between them. When voltage is applied, positive and negative charges accumulate on the electrodes. This storage capacity is known as the capacitor’s “capacitance,” measured in farads. Simply put, it’s a device that stores electricity in a different way than a battery.
Differences between capacitors and batteries.
The main difference between capacitors and batteries lies in their mechanisms for storing and releasing energy. Capacitors physically store electrical charge and can release it instantly, allowing for rapid charging and discharging, suitable for peak power demands. Conversely, batteries store energy chemically and release it gradually, making them ideal for long-term energy supply and sustained, low-power usage.
Examples of capacitor use.
Capacitors have a wide range of applications. In electronic circuits, they are used for signal smoothing, filtering, and timing control. In power circuits, they support stable power supply. In energy regeneration systems like those in electric vehicles, they temporarily store energy generated during braking and reuse it for acceleration. Research in the automotive sector is quite active. Current EVs and HVs have a regeneration efficiency of up to 60%, with significant losses. Using capacitors, alone or in conjunction with batteries, can extend the range of EVs and HVs.
In addition to the aforementioned uses, capacitors are also applied in solar power generation, wind power, and audio equipment. In modern society, capacitors are indispensable for energy management, improving power quality, and efficient power usage.
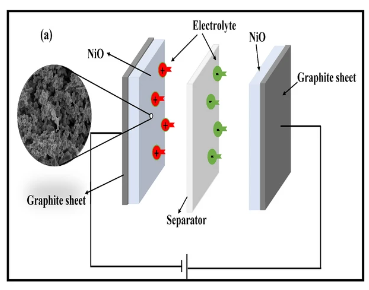
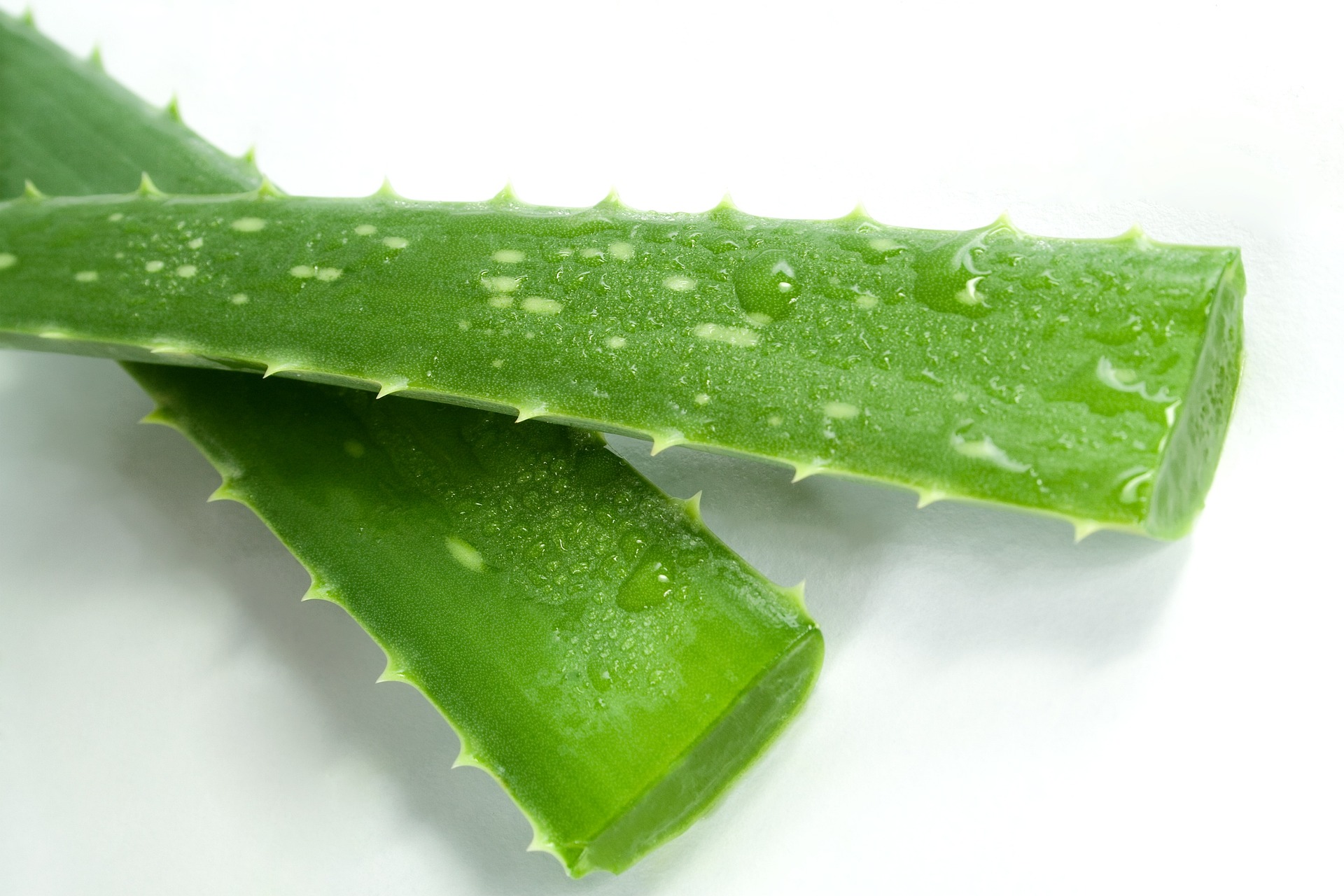
Capacitors made from aloe vera.
Capacitors have drawbacks, such as lower capacitance per volume compared to batteries, voltage drop when overcharged, and lifespan varying with the charge-discharge cycle. High cost also poses a significant hurdle in societal applications.
However, the study introduced here might offer a solution.
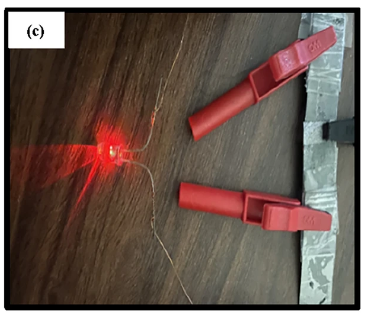
It involves synthesizing nickel oxide nanoparticles using aloe vera leaf extract as a material for capacitors. Aloe vera is abundant in nature and easy to extract, reducing costs. Capacitors produced this way have higher capacitance and better charge-discharge efficiency than conventional ones. Additionally, this method features an environmentally friendly and sustainable manufacturing process, presenting a promising approach to overcoming the cost and performance challenges of capacitors.

Preparing for the rise in capacitor demand.
Capacitors are expected to become increasingly important in numerous sectors, including efficient use of renewable energy sources, energy management in electric vehicles, power supply for portable electronic devices, and power quality management in industry. The demand will likely grow, especially in areas where efficient energy storage and rapid release are crucial.
To anticipate this rising demand, applying capacitors in fields like renewable energy, electric vehicles, electronics, and industrial power management is vital. Developing high-performance, cost-effective capacitors will be key in these areas.
In the future, “aloe capacitors” might play a significant role in supporting our lives.




コメント