Salvia contains various active ingredients.
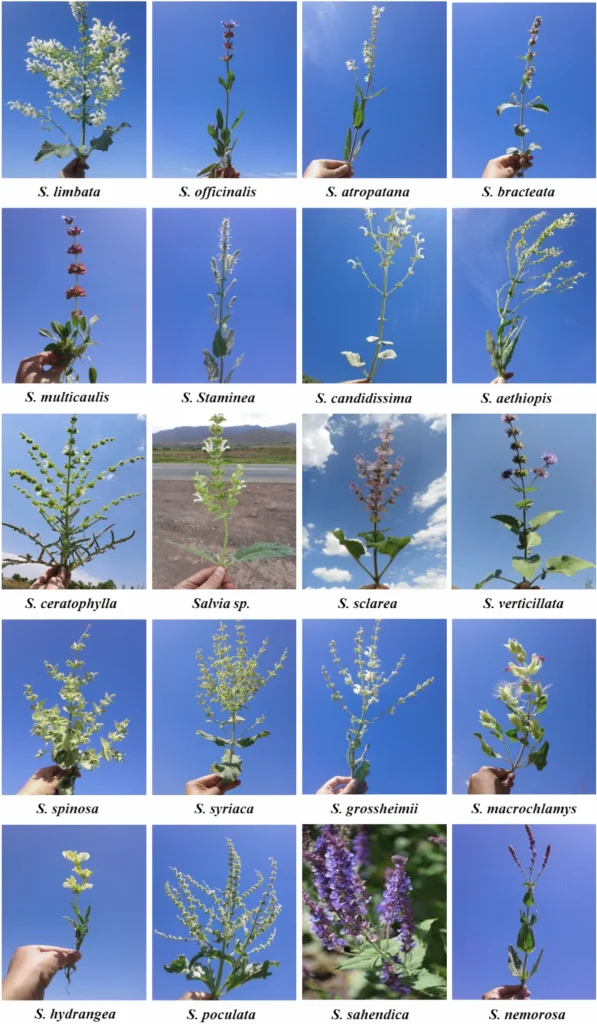
The Lamiaceae family is a group composed of about 250 genera and 7000 species worldwide. Among them, Salvia is one of the largest and most valuable genera in the Lamiaceae family, with more than 1000 species distributed worldwide. The reason it is valuable is that it has been said to have various medicinal effects such as antispasmodic, antiseptic, antiperspirant, anti-inflammatory, treatment of mental illnesses, and neurological disorders in traditional medicine, and it is beginning to broaden its scope of application even in modern times. The paper introduced today comprehensively investigated the extracts of 102 species of Salvia from Iran using modern technology to explore the potential of Salvia. It revealed the potential of new treatments for diseases that had not been confirmed before.

Investigating Salvia
The investigation of Salvia covered various items. The content of phenols, flavonoids, tannins, photosynthetic pigments, and ascorbic acid, as well as antioxidant activity, were measured. Furthermore, 40 types of compounds were identified and labeled for each variety. It was found that Salvia has a diversity not only in appearance but also in its composition, with slightly different components. Since it was found that Salvia contains various types of components, an investigation is being conducted to see what kind of diseases it might be effective against based on the combination of components.
Diverse Effects Can Be Expected from the Combination of Components!
For example, varieties with high content of syringic acid can be expected to have cardioprotective, hepatoprotective, antidiabetic, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and apoptosis-promoting effects. Additionally, species rich in salvianolic acid and lithospermic acid are promising for the treatment of endothelial dysfunction, pulmonary arterial hypertension, and cardiac fibrosis. Other species containing high amounts of ferulic acid can be expected to have cardioprotective, antifibrotic, anti-apoptotic, and antiplatelet effects. Species rich in flavonoid glycosides and glucuronic acid conjugates showed diverse potentials such as antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, antistress, antiallergic, antiviral, and antibacterial activities.
Furthermore, combining extracts from different species can lead to new medicinal effects. Combining extracts from species containing high amounts of specific compounds like salvianolic acid A and salvianolic acid B with extracts from species rich in rosmarinic acid and salvianolic acid C is said to have the potential to contribute to the treatment of “Alzheimer’s disease”. Isn’t it a treasure trove of possibilities?
It Is an Era to Explore Efficacy from the Combination of Multiple Components
Western medicine, from which we often benefit, has effectively utilized the therapeutic effects of single components. On the other hand, Eastern medicine, such as traditional Chinese medicine, has treated people with combined effects of various “medicinal herbs”. Although new components are still being registered as medicines today, I feel that an era has come where more diverse treatments are required. This is because, as the world population increases, more efficient healthcare is required for everyone to enjoy public health worldwide. Like in the example of Salvia this time, new uses might be explored even in plants that have been used so far by “combining” them. Plants have always been, and will continue to be, a treasure trove of possibilities.

多成分の組み合わせから効能を探る時代だ
私たちが恩恵を受けることの多い西洋医学では、単一の成分による治癒効果を有効活用してきました。他方、中医学を例とする東洋医学では、さまざまな「生薬」の組み合わせにより、複合的な効果で人を治療してきました。現在でも新しい成分が薬として登録されているものの、より多様な治療が求められる時代になっているように感じます。それは、世界人口が増え、公衆衛生を世界中すべての人が享受するためにはより効率的な医療が求められているからだと考えています。今回のサルビアの例のように、これまで使っていた植物の中にも、「組み合わせる」ことにより新しい使い方が模索できるかもしれません。これまでも、これからも植物は可能性の宝庫ですね。


コメント