In recent years, the impact of climate change on agriculture has become increasingly severe. In particular, in low-latitude regions, the growing environment for crops is undergoing significant changes, raising concerns about the loss of diversity. Based on the latest research paper, let’s explore the impact of climate change on crop diversity in low-latitude regions and the potential issues that may arise in the future.
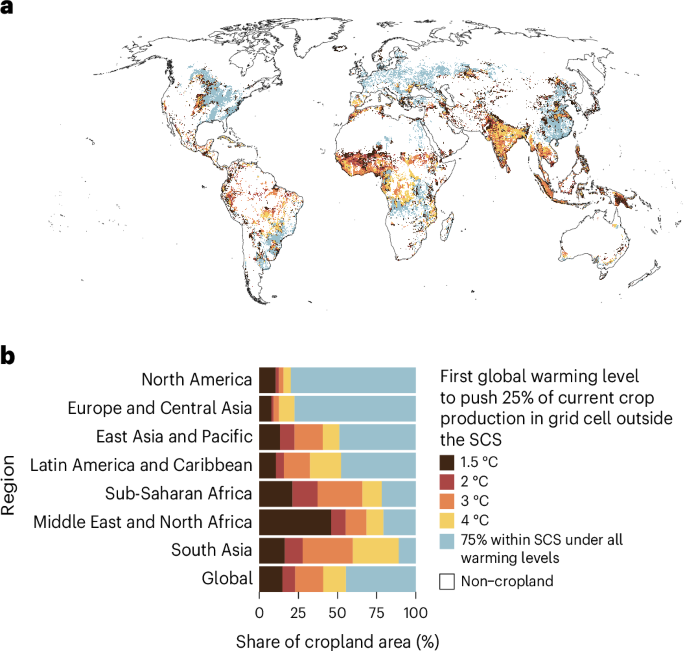
Decline in Crop Diversity in Low-Latitude Regions
Issue: Low-latitude regions are the center of global crop diversity, where many traditional crops are cultivated. However, rising temperatures and changes in precipitation patterns may shrink the suitable environment for their growth.
Impact:
- Traditional crops may no longer adapt, leading to the collapse of local food cultures and agricultural ecosystems.
- The suitable areas for crops may shift to higher latitudes, causing the decline of agriculture in low-latitude regions.
Changes in the Growth Range of Major Crops
Issue: Major crops important in low-latitude regions (such as maize, rice, wheat, bananas, and cacao) may face a reduction in suitable environments in the future.
Impact:
- Declining yields will lead to a decrease in farmers’ income.
- Changes in suitable areas may leave producers in low-latitude regions at a competitive disadvantage.
- Global food supply will also be affected, causing fluctuations in food prices.
Loss of Genetic Diversity
Issue: Crop varieties unique to low-latitude regions may disappear, leading to a decline in genetic diversity.
Impact:
- The number of crops with low resistance to pests, diseases, and climate change will increase, raising overall agricultural risks.
- The loss of traditional crops will reduce future breeding and crop improvement options.
Impact on Agricultural Labor and Livelihoods
Issue: Declines in crop yields and reductions in arable land due to climate change will destabilize farmers’ livelihoods.
Impact:
- Many farmers will no longer be able to continue farming, leading to increased migration to urban areas.
- The collapse of small-scale farms will trigger economic decline in rural communities.
- Vulnerable populations, including women and smallholder farmers, will be most severely affected.
Risks to Food Security
Issue: The decline in crop production in low-latitude regions will cause instability in food supply.
Impact:
- Rising food prices will increase the cost of living.
- The loss of high-nutrient traditional crops will lead to an imbalanced diet and nutritional deficiencies.
- If the development of climate adaptation technologies is delayed, the risk of global food shortages will increase.
The Need for Adaptation Strategies
To address these challenges, the following adaptation strategies are essential:
1. Development of Climate-Resilient Crop Varieties
Developing and introducing crop varieties with high heat and drought resistance.
2. Introduction of Sustainable Agricultural Technologies
Promoting environmentally friendly agriculture through agroforestry and precision farming technologies.
3. Policy Support and Farmer Education
Providing adaptation technologies and necessary financial support to farmers through government and international organizations.
4. Conservation of Genetic Resources
Preserving crop genetic diversity through the establishment of seed banks and protection of traditional varieties.
Conclusion
The impact of climate change on crop diversity in low-latitude regions is severe, and the following issues are expected to become prominent in the future:
- Decline in crop diversity → Loss of traditional crops
- Shifts in major crop growth areas → Decline of agriculture in low-latitude regions
- Loss of genetic diversity → Reduced adaptability to climate change
- Instability in agricultural labor and livelihoods → Increased poverty among farmers
- Increased risks to food security → Rising prices and worsening nutritional deficiencies
- The necessity of adaptation strategies → Promotion of technological innovation and policy support
To address these issues, the implementation of adaptation strategies based on scientific knowledge and international cooperation is essential. It is crucial to consider actions now to achieve sustainable agriculture.


コメント