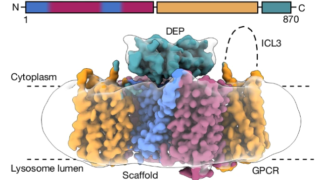
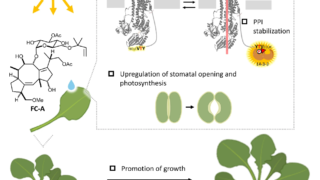
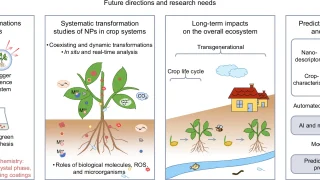
 Research
Research How Different Are Japanese and Global Soybeans? Surprising Insights from Genomic Analysis and the Latest Findings in Soybean Breeding.
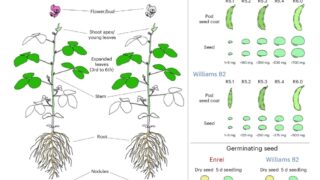
A new Nature Genetics study reveals major genomic differences between Japanese and global soybean varieties. Discover how structural variants in key genes like PDH1 and GmFT2b affect pod shattering, flowering time, and seed size—reshaping the path to next-generation crop breeding.